Ever wonder what goes into that everyday tube of toothpaste? Discover the fascinating factory process behind your daily smile.
Ever grab your toothbrush in the morning and squeeze out that perfect ribbon of toothpaste without thinking twice about where it came from? Most of us use it every day, but the behind-the-scenes process of making toothpaste is actually pretty fascinating. It’s a blend of chemistry, careful mixing, and high-tech machinery that turns simple ingredients into the paste that keeps our smiles bright and healthy. Whether you’re curious about what’s really in that tube or how those cool stripes show up, this guide breaks it all down in an easy-to-follow way. We’ll cover the ingredients, the step-by-step factory process, special tricks like striped toothpaste, the equipment involved, and answer some of the most common questions people have.
What Are the Main Ingredients in Toothpaste?
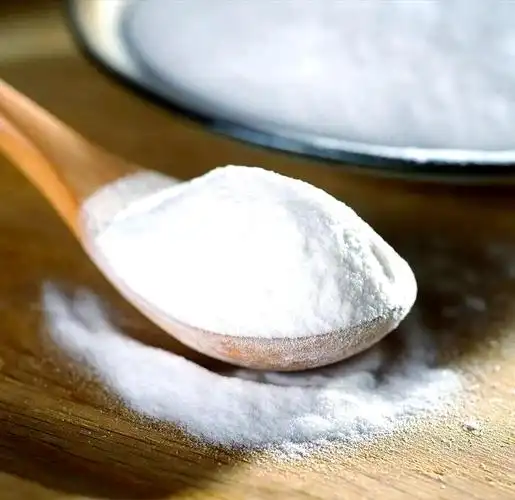

Toothpaste isn’t just one thing—it’s a carefully balanced mix of ingredients that clean, protect, and freshen your teeth and gums. Manufacturers tweak the formula depending on the type (like whitening, sensitive, or kids‘), but most toothpastes share the same core components. Here’s a straightforward breakdown:
- Abrasives (around 50% of the paste): These are the gentle scrubbers, like hydrated silica or calcium carbonate. They polish away stains and plaque without damaging enamel—think of them as tiny, safe sandpaper for your teeth.
- Humectants (20-40%): Glycerin or sorbitol keep the paste moist and prevent it from drying out in the tube. Without them, your toothpaste would turn into a hard brick.
- Water (20-40%): The base that holds everything together and makes it spreadable.
- Fluoride: The star player for cavity prevention, usually sodium fluoride or stannous fluoride. It strengthens enamel and fights bacteria.
- Detergents/Foaming Agents: Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) creates that satisfying foam when you brush. Some brands skip it for “SLS-free” versions.
- Thickeners and Binders: Things like carrageenan or cellulose gum give toothpaste its smooth, gel-like texture.
- Flavors and Sweeteners: Mint, cinnamon, or bubblegum flavors (from essential oils) plus non-cavity-causing sweeteners like xylitol or saccharin make brushing enjoyable.
- Preservatives and Colors: Small amounts keep it fresh and give it that classic white or striped look.
All these are FDA-approved and safe in the right amounts. Fun fact: Modern toothpastes are vegan-friendly—no animal bones or anything weird like ancient recipes used!
Step-by-Step Toothpaste Manufacturing Process
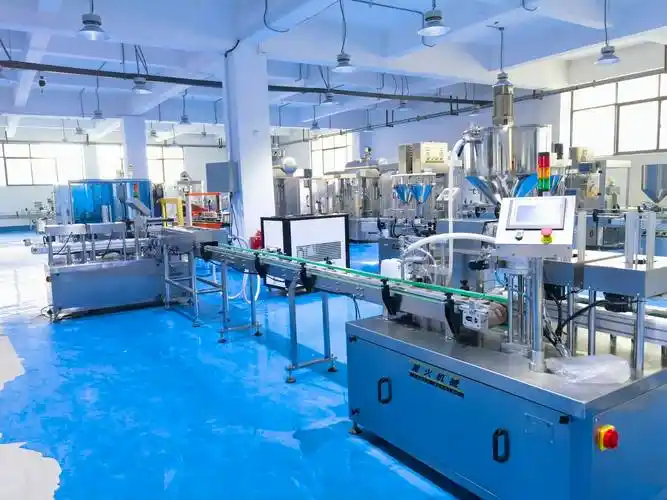

Making toothpaste happens in big, clean factories with strict quality controls. A single batch can produce thousands of tubes! The process is precise to avoid air bubbles or lumps. Here’s how it typically goes:
- Raw Material Preparation: Everything starts with weighing and checking ingredients. Powders like abrasives and fluoride are stored in silos, while liquids like water and humectants come in tanks. Quality checks ensure purity.
- Mixing the Liquid Base: In a huge stainless steel tank, water, humectants, and binders are blended first. This creates a smooth base.
- Adding Thickeners and Binders: Gums and thickeners go in next under high-speed mixing to build viscosity.
- Incorporating Abrasives: The gritty stuff (silica, etc.) is slowly added while the mixer runs. This step prevents clumping.
- Adding Active Ingredients: Fluoride and other therapeutics are mixed in carefully—too much heat or air can ruin their effectiveness.
- Flavoring and Final Blending: Flavors, sweeteners, detergents, and colors are added last. The whole mix happens under vacuum to remove air bubbles that could make the paste gritty or cause tubes to burst.
- Quality Testing: Samples are tested for texture, pH, fluoride levels, and microbe safety.
- Tube Filling: The finished paste is pumped into tubes, which are then sealed, capped, and boxed.
The whole thing is automated and hygienic—factories follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) to keep everything spotless.
How Are Stripes Added to Toothpaste?
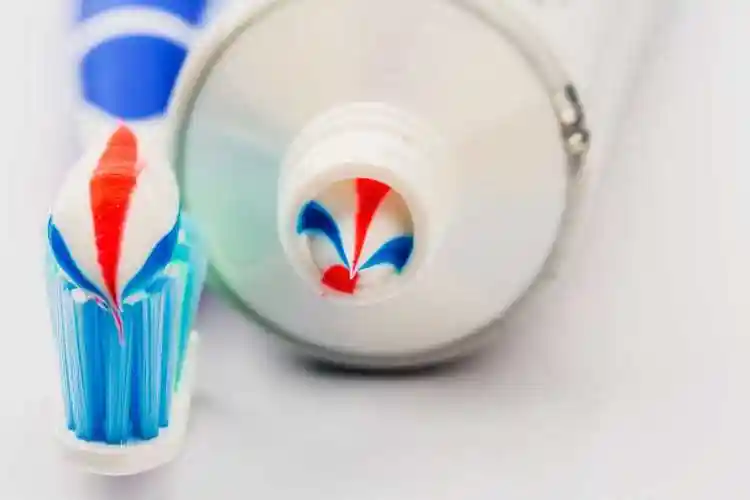
One of the coolest parts—those perfect red, blue, or green stripes! It’s not magic; it’s clever engineering. The main white paste fills most of the tube. The stripe color (usually a thicker gel with color and sometimes extra ingredients like baking soda) is stored in a separate small tube or chamber inside the nozzle.
When you squeeze, pressure pushes the white paste through the main opening, while the stripe gel flows through tiny side holes. They merge just right at the tip, creating stripes that hold their shape because the gels have different viscosities. No mixing inside the tube—it stays separated until you brush!
What Equipment Is Used in Toothpaste Factories?
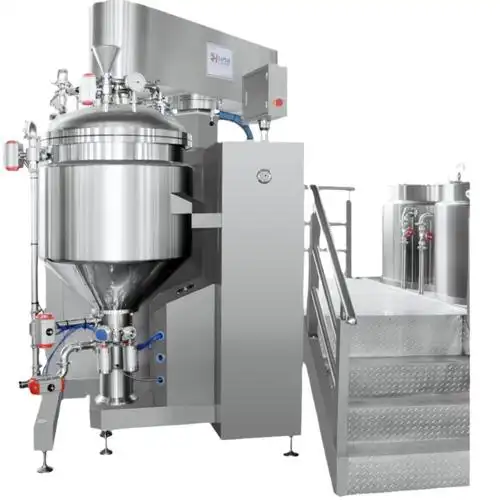

Toothpaste production relies on specialized machines for efficiency and consistency:
- Vacuum Mixers/Homogenizers: Massive tanks (up to thousands of liters) with high-shear blades that mix under vacuum. This prevents air pockets and ensures smoothness.
- Powder-Liquid Blenders: For evenly dispersing abrasives without lumps.
- Tube Filling and Sealing Machines: Automated lines that fill, seal the bottom, add caps, and print dates—all at high speed (hundreds of tubes per minute).
- Packaging Lines: Robots box tubes into cartons and pallets for shipping.
These machines are stainless steel, easy to clean, and computer-controlled for precision.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is toothpaste made in a factory?
It’s a multi-step mixing process under vacuum in large stainless-steel tanks, followed by automated tube filling—all in super-clean facilities following strict hygiene standards.
Who invented modern toothpaste?
Dr. Washington Sheffield introduced the first creme dentifrice in the 1850s, and collapsible tubes were popularized in the 1890s. Colgate began mass production shortly after.
Is toothpaste made from animal bones?
No, that’s a myth from ancient recipes. Modern toothpaste uses mineral abrasives like hydrated silica or calcium carbonate—no animal products.
Where is most toothpaste manufactured?
Major brands like Colgate, Crest (Procter & Gamble), and others produce in factories across the US, China, India, Europe, and other regions worldwide.
Why does toothpaste foam when brushing?
Detergents like sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) create foam to help spread cleaning agents around your mouth and give that fresh, clean feeling.
Can you make toothpaste at home?
Yes, simple DIY recipes use baking soda, coconut oil, and xylitol, but they lack fluoride and the professional strength of commercial versions.
How long does toothpaste last in the tube?
Typically 2-3 years unopened. Always check the expiration date printed on the tube.
Why is fluoride added to toothpaste?
Fluoride remineralizes tooth enamel, strengthens teeth, and reduces cavity risk by up to 25%.
How do factories prevent air bubbles in toothpaste?
The mixing process uses vacuum homogenizers to remove air, ensuring a smooth texture and preventing tubes from bursting.
How much toothpaste does a factory produce daily?
Large plants can produce millions of tubes per day, with single batches often filling tens of thousands of tubes.
Is gel toothpaste manufactured differently from regular paste?
The process is similar, but gels use different thickeners and fewer or clearer abrasives for a transparent look.
What is the history of toothpaste?
Ancient civilizations used mixtures like crushed bones and salt. Modern toothpaste in tubes began in the late 1800s, with fluoride added in the mid-20th century.
Are toothpaste tubes recyclable?
Many brands now use recyclable aluminum or plastic tubes, and programs exist for hard-to-recycle ones through partnerships like TC.
What are common challenges in toothpaste manufacturing?
Preventing aeration (air bubbles), achieving the right viscosity, evenly dispersing abrasives, and maintaining strict hygiene standards.
Is swallowing toothpaste dangerous?
In small amounts (like during brushing), it’s generally safe for adults, but kids should spit it out to avoid excess fluoride ingestion.
How has toothpaste manufacturing evolved?
From manual jar filling to highly automated vacuum mixing and high-speed tube filling, with modern focus on sustainability and specialized formulas.
Next time you brush, you’ll appreciate the science in that squeeze. Toothpaste manufacturing combines everyday ingredients with smart tech to keep oral care simple and effective. Keep smiling!
Data Source: Guangzhou Toothpaste Manufacturers


